When the electrical equipment is in use, if the insulation damage or breakdown of the equipment causes the outer casing to be charged, the human body may have electric shock when it touches the outer casing. To this end, electrical equipment must be reliably electrically connected to the ground, ie grounding protection, to protect the human body from electric shock.
(1) Concept and principle of protective grounding 1 The concept of protective grounding is grounding to ensure its normal operation; protective grounding refers to a grounding form that protects the human body from contact with exposed parts of the equipment and is electrically shocked. In a neutral point ungrounded system, the exposed part of the equipment (metal casing or metal frame) must be reliably electrically connected to the earth, ie protective earthing. The neutral point grounding of the three-phase generator or transformer belongs to the working ground. The grounding device consists of the grounding body and the grounding wire. The metal conductor buried in the ground and directly in contact with the earth is called the grounding body. The grounding body and the grounding bolt of the electrical equipment are connected. The metal conductor is called the ground wire. The sum of the grounding resistance of the grounding body and the grounding wire resistance is called the grounding resistance of the grounding device.
2 Principle of protective grounding In the neutral point ungrounded system, the equipment casing is not grounded and accidentally charged, there is voltage between the outer casing and the earth, the human body touches the outer casing, and the human body will have a capacitor current flowing. In this way, the human body suffers from electric shock. If the case is grounded, the human body and the ground body are connected in parallel with the resistor, and the current flowing through each path will be inversely proportional to the magnitude of its resistance. The body resistance is much larger than the grounding body resistance. The body resistance is usually 600 to 1000 ohms, the grounding resistance is usually less than 4Q, and the current flowing through the human body is small, so that the human body can be completely safe.
The protective earthing is suitable for low-voltage networks where the neutral point is not grounded. In an ungrounded power grid, the use of protective grounding allows the human body to avoid electric shock accidents due to the relatively small current per ground. However, in a neutral-grounded power grid, because the single-phase ground current is large, the protective grounding cannot completely avoid the danger of human body electric shock, but the protection is connected to zero.
(2) Concept and principle of protection and zero connection 1. Concept of protection and zero connection Protection and zero connection means that in the system where the neutral point of the power supply is grounded, the exposed part of the equipment to be grounded is directly connected with the neutral line of the power supply, which is equivalent to setting each The exposed part is electrically connected to the earth.
2 Working principle of protection and zero connection When the equipment works normally, the exposed part is not charged, and the human body touches the outer casing to touch the zero line, no danger, as shown in Figure (a). When using protective zero connection, it should be noted that it is not advisable to mix the protective grounding and protection with zero, and the working grounding of the neutral point must be reliable.
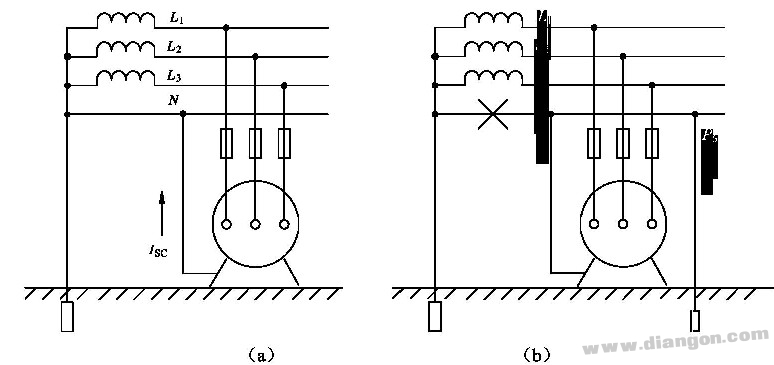
Figure protection zero working principle circuit 3 Repeated grounding In the system where the neutral line of the power supply has been working grounded, in order to ensure the reliability of the protection zero connection, it is necessary to re-ground the neutral line or the ground line at a certain distance, which is called repeated grounding. .
It can be seen from the figure (a) that once the neutral line is broken, the exposed part of the device is charged, and the human body may also have the possibility of electric shock. In the repeated grounding system, as shown in Figure (b), even if the neutral wire breaks, the exposed part is greatly reduced due to repeated grounding, and the damage to the human body is greatly reduced. However, it should be avoided to avoid the disconnection of the neutral or grounding wire.
(3) Leakage protection Leakage protection is a new protection against electric shock that has been promoted in recent years. In the electrical equipment, leakage or grounding fault occurs and the human body has not touched the time. The leakage protection device has cut off the power supply; when the human body has touched the charged body, the leakage protector can cut off the power supply in a very short time and reduce the harm to the human body. There are many types of leakage protectors. At present, transistor-amplified leakage protectors are widely used.
RF is any frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum associated with the propagation of radio waves. When RF current is supplied to the antenna, an electromagnetic field is created, which is then able to propagate or propagate through space. Many wireless technologies are based on radio frequency field propagation. These frequencies form part of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum.
RF coaxial cables are cables that transmit electromagnetic energy in the radio frequency range. Radio frequency cables are indispensable components in various radio communication systems and electronic equipment. They are widely used in wireless communication and broadcasting, television, radar, navigation, computers and instruments.
RF coaxial cable is the most commonly used construction type. Because the inner and outer conductors are in concentric positions, the electromagnetic energy is limited to propagate in the medium between the inner and outer conductors, so it has significant advantages such as small attenuation, high shielding performance, wide operating frequency bandwidth and stable performance. Typically used to transmit radio frequency energy from 500 kHz to 18 GHz. At present, there are two types of commonly used RF coaxial cables: 50Ω and 75Ω RF coaxial cables. The characteristic impedance of 75Ω RF coaxial cable is often used in CATV network, so it is called CATV cable, and the transmission bandwidth can reach 1GHz. At present, the transmission bandwidth of commonly used CATV cable is 750MHz.
Welcome to contact our sales and engineers to discuss your products together!

RF Coaxial Cable Assembly,Cable Harness,Custom Wire Harness,Cable Assembly RF Coaxial
Kable-X Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd , https://www.kable-x-tech.com
