A RAKE receiver is a final receiver that separates multipath signals and efficiently combines the energy of multipath signals.
RAKE receiving technology is an important technology in the third generation CDMA mobile communication system. In the CDMA mobile communication system, due to the wide signal bandwidth, there are complex multipath radio signals, and communication is affected by multipath fading. The RAKE receiving technology is actually a multipath diversity receiving technology, which can distinguish fine multipath signals in time, and weight-modulate these resolved multipath signals to form a strengthened signal. Since the transversal filter in the receiver has a saw-like tap like a dice, the receiver is called a RAKE receiver.

Diversity technology is a technique to study how to make full use of the multipath signal energy in transmission to improve transmission reliability. It is also a technique for studying how to use the basic parameters of the signal in the time domain, the frequency domain and the air domain, how to spread it and how to collect it.
In order to obtain different paths that are almost independent of each other at the receiving end, it can be implemented by different angles of airspace, time domain, frequency domain, different methods and measures. The most basic ones are as follows:
1. Space diversity:
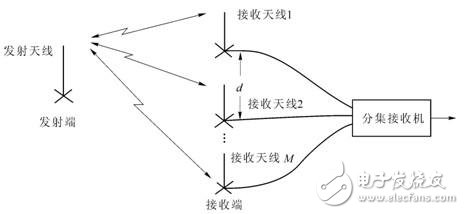
1) The anti-fading function is realized by the independence of signal fading received by different receiving locations (spaces).
2) The basic structure of spatial diversity is: one antenna is sent at the originating end, and the N antenna is received at the receiving end.
3) The distance d between the receiving antennas is sufficiently large to be greater than the coherence distance ΔR.
4) The larger the diversity antenna number N, the better the diversity effect, but the diversity and diversity are very different and belong to the qualitative change. The diversity gain is proportional to the number N of diversity, the improvement is limited, is a quantitative change, and the degree of improvement decreases as the number of diversity increases. Engineering compromise, generally take N = 2 ~ 4.
5) There are two types of changes in spatial diversity:
a) Polarization diversity: it uses signals from two antennas that are orthogonal to each other at the same location to exhibit uncorrelated fading characteristics for diversity reception, that is, to install horizontal and vertical polarization antennas on the transceiver antenna. The obtained two signals with irrelevant fading characteristics can be polarization-diversity. Advantages: compact structure and space saving; disadvantages: 3dB loss due to the transmission power to be distributed to the two antennas.
b) Angle diversity: Due to the different terrain, terrain and receiving environment, the signals arriving at different paths of the receiving end may come from different directions, so that directional antennas can be used at the receiving end to point to different directions of arrival. The multipath signals received by each directional antenna are irrelevant.
2. Frequency diversity:
1) The information to be transmitted is separately modulated onto different carriers and sent to the channel.
2) The spacing between the different carriers is sufficiently large to be greater than the frequency coherence bandwidth ΔF.
3) Compared with spatial diversity, frequency diversity has the advantage of reducing the number of receiving antennas and corresponding devices; the disadvantage is that it occupies more spectrum resources, and it is possible to use multiple transmitters at the origin.
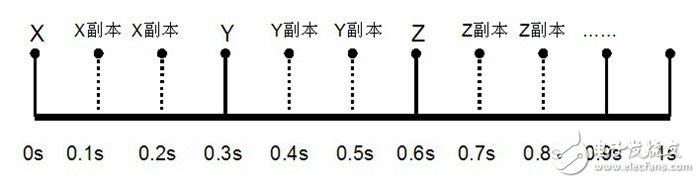
3. Time diversity:
1) For a random fading signal, if the sampling interval is large enough, the fading between the two samples is incompatible with each other.
Off, this feature can be used to form time diversity.
2) The signals to be transmitted are repeatedly transmitted at regular intervals, and N independent diversity branches can be obtained at the receiving end.
3) The time interval Δt should be greater than the coherence time ΔT in the time domain. Time diversity is useless for mobile stations that are at rest.
4) Compared with spatial diversity, time diversity has the advantage of reducing the number of receiving antennas. The disadvantage is that it takes up more time slot resources, thus reducing transmission efficiency.
The advantages of diversity technology are very powerful, and diversity techniques are used in many communication systems. Moreover, it should be emphasized here that the use of more than one diversity method in a communication system is not an exhaustive one. For example, in the IS-95 system, spatial diversity, frequency diversity, and time diversity techniques are simultaneously used, and their purpose is to obtain the required bit error rate with a minimum transmission probability. RAKE receivers are time diversity and are used to overcome multipath interference.
The basic principle of the RAKE receiver is to take out the multipath components whose amplitude is significantly larger than the noise background, delay and phase correct it, align it at a certain moment, merge them according to certain rules, and merge the variable vectors into algebras. Summing, effectively utilizing multipath components, and improving the effect of multipath diversity.
Due to the random mobility of the user, the number, magnitude, delay, and phase of the received multipath components are random quantities.
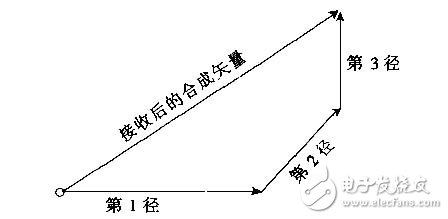
If there is no RAKE receiver, the multipath signal is synthesized as shown in the figure above. If a RAKE receiver is used, the multipath signal is synthesized as shown below.
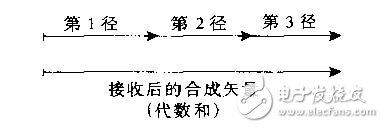
It can be seen that the RAKE reception separates the paths, phase calibration, and utilization, and the variable vectors are added as algebraic additions, effectively utilizing the multipath components.
According to the concept of separable paths in a CDMA system, when the multipath delay of the two signals differs by more than one spread chip width, the two signals can be considered as uncorrelated or otherwise separable. When the response is in the frequency domain, that is, when the transmission bandwidth of the signal is greater than the coherence bandwidth of the signal, the two signals are considered to be irrelevant, or the paths are separable. Since the CDMA system is broadband transmission, all channels share frequency resources, so the CDMA system can use the RAKE receiving technology, while the other two multiple access technologies TDMA and FDMA cannot be used.
The metric of RAKE receiver diversity depends on the multipath delay width and the ability to multipath separation.
In a multipath fading channel with a maximum delay spread of m, the concept of RAKE is to use a specific wideband transmission signal whose bandwidth W is much larger than the coherence bandwidth m of the channel, according to the concept of separable multipath. The number of multipaths that can be separated in the case is. Therefore, the RAKE receiver adopts L correlators, and the difference between the delays processed by the adjacent correlators is 1/W, and each correlator extracts only the part of the multipath signal of the corresponding delay from the total received signal.
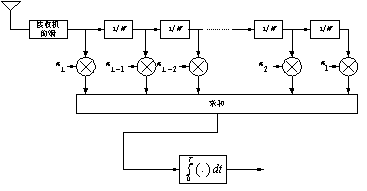
Block diagram of the RAKE receiver
Diversity reception technology is an important technique against multipath fading. The premise of using diversity reception techniques is that the fading of the multipath components of the system are independent of each other. In the same communication system, multiple diversity methods can be used simultaneously to reduce the bit error rate. The RAKE receiver collects the energy in the multipath by combining the separable multipaths proportionally to their intensities.
In summary, diversity receiving technology and RAKE receiver are important technologies in mobile communication systems. In the third generation mobile communication systems, these two technologies have been more widely used.
Power Film Capacitors - Plastic Case
Polypropylene High Voltage Capacitor,axial film capacitor,axial capacitor,SHV capacitor
XIAN STATE IMPORT & EXPORT CORP. , https://www.shvcomponents.com
