 1. What is the capacity of the transformer?
1. What is the capacity of the transformer? From the above analysis of the second problem, it can be seen that the selection of the core is related to the voltage, and the choice of the conductor is related to the current, that is, the thickness of the conductor is directly related to the amount of heat generated. In other words, the capacity of the transformer is only related to the amount of heat generated. For a well-designed transformer, if it is working in a poorly-cooled environment, if it is 1000KVA, it may work at 1250KVA if the cooling capacity is enhanced. In addition, the nominal capacity of the transformer is also related to the allowed temperature rise. For example, if a 1000KVA transformer allows a temperature rise of 100K, if it can be allowed to work up to 120K under special circumstances, the capacity is more than 1000KVA. . It can also be seen that if the heat dissipation conditions of the transformer are improved, its nominal capacity can be increased. Conversely, for the same capacity inverter, the size of the transformer cabinet can be reduced.
Therefore, in some bidding processes, the competitors intentionally designate a larger transformer capacity, giving the user a large margin of illusion design, in fact, there is no sense, the key depends on the size and cooling method of the transformer.
2. What are the cooling mediums of the rectifier transformer?
To bring heat out of the inverter, there are generally three types of media that can be used: air, water, and oil. The heating components of the high-voltage inverter are mainly two parts: one is a rectifier transformer and the other is a power element. In the early stage of the transformer, the oil cooling method was mainly adopted, ie, the transformer was immersed in the oil tank. Since the specific heat of the oil is higher than air and the insulation strength is high, this heat dissipation method is the main heat dissipation of the high-power transformer. However, due to the need for maintenance of the oil product, the seal at the lead-out line is not well resolved. With the advancement of insulating materials, dry-type transformers have dominated the medium and low power levels. Dry-type transformers are cooled by air. The transformer can also be water-cooled, that is, the coil of the transformer is made hollow, and the interior of the transformer is pure water, and pure water is used to take away the heat.
3. What are the basic problems in transformer design?
The basic problem of transformer design is magnetic flux and current density. The current and the capacity of the transformer are proportional to each other, and the magnitude of the current density (ie, the thickness of the wire) is taken into consideration in terms of the amount of heat generated by the conductor. For magnetic flux, the basic relation of electromagnetism is u = 4.44fwΦ, where u is the voltage; f is the frequency, here is 50Hz, the fixed value; w is the number of turns of the coil; Φ is the magnetic flux. Since the magnetic flux density B of the silicon steel sheet is limited by the material, generally only 1.4-1.8 Tesla can be designed, and Φ=BS. Therefore, to increase Φ, the sectional area of ​​the core can generally only be increased. The core of the transformer is generally a three-phase column. The cross-sectional area of ​​the core can be determined according to the above formula. The size of the core window must consider the principle of putting the coil in. The larger the capacity of the transformer, the thicker the wire, the larger the core's window needs to be. China Power Electronics Industry Network In the transformer design, the amount of copper and iron can be balanced. Because once the capacity of the transformer is determined, the current is determined, and the thickness of the wire is also determined. By increasing the number of turns W, the magnetic flux Φ can be smaller, and the cross-sectional area of ​​the core can be smaller, but these must be reduced. The number of turns of the iron core is larger. On the other hand, reducing the number of turns, the magnetic flux Φ is larger, and the cross-sectional area of ​​the iron core is larger, but the window of the iron core can be smaller.
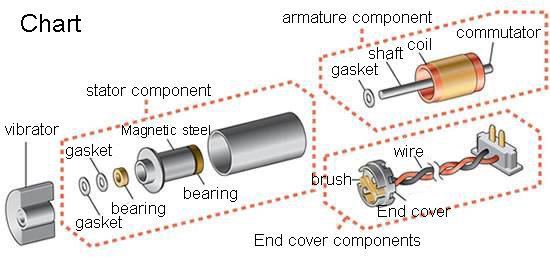
Coreless Motor product introduction:
Coreless Motor, small size, light weight (cylinder) - radial rotation/weeks to rotation (flat) - low noise, low power consumption, strong sense of vibration - simple structure - reliability - response time short Micro Vibration Motor is mainly used in mobile phones, toys, adult health supplies, etc
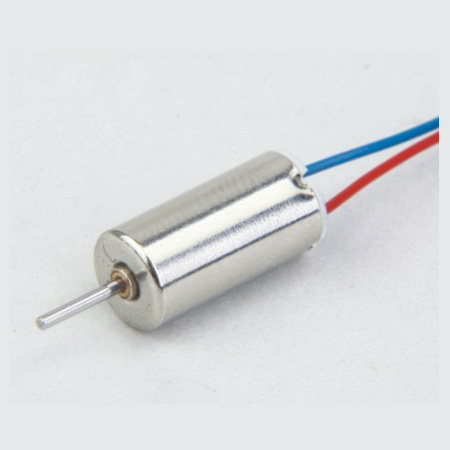
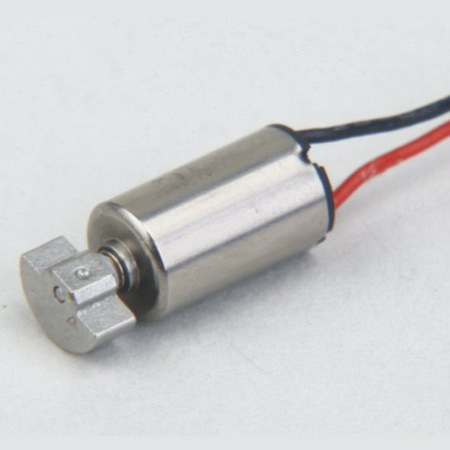
Function: fast speed, suitable for aircraft model, electric toothbrush,USB fan and other products.

Characteristic: the volume is 6MM 7MM fast.
Features: small size, fast speed, dc high speed motor starting voltage 0.6v is not possible for other motors.Wear shaking head, strong vibration feeling.
Operating temperature range:
Coreless Motor should be used at a temperature of -10~60℃.
The figures stated in the catalog specifications are based on use at ordinary room temperature catalog specifications re based on use at ordinary room temperature (approximately20~25℃.
If a Coreless Motor is used outside the prescribed temperature range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.Depending on the temperature conditions ,it may be possible to deal with them by changing the grease of the motor's parts.Please feel free to consult with us about this.
Storage temperature range:
Coreless Motor should be stored ta a temperature of -15~65℃.
In case of storage outside this range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.
Service life:
The longevity of Coreless Motor is greatly affected by the load conditions , the mode of operation,the environment of use ,etc.Therefore,it is necessary to check the conditions under which the product will actually be used .The following conditions will have a negative effect on longevity.Please consult with us should any of them apply.â—Use with a load that exceeds the rated torque
â—Frequent starting
â—Momentary reversals of turning direction
â—Impact loads
â—Long-term continuous operation
â—Forced turning using the output shaft
â—Use in which the permitted overhang load or the permitted thrust load is exceeded
â—A pulse drive ,e.g.,a short break,counter electromotive force,PWM control
â—Use of a voltage that is nonstandard as regards the rated voltage
â—Use outside the prescribed temperature or relative-humidity range,or in a special environment.
â—Please consult with us about these or any other conditions of use that may apply,so that we can be sure that you select the most appropriate model.
when it come to volume production,we're a major player as well .each month,we rurn out 600000 units,all of which are compliant with the rohs directive.Have any questions or special needed, please contact us, we have the engineer group and best sales department to service to you Looking forward to your inquiry. Welcome to our factory.

Coreless Motor
Coreless Motor,Micro Coreless Motor,7Mm Coreless Motor,Micro 6Mm Coreless Motor
Shenzhen Shunchang Motor Co., LTD. , https://www.scgearmotor.com
