introduction
Saving energy is an important issue in the future. As a new type of green lighting source, LED is bound to be the future development trend. However, in the LED development process, the lighting designer lacks understanding of a series of psychological, physiological and other effects of various color light effects on human vision, resulting in problems in photobiosafety.
1 LED lighting color space unevenness problem
1.1 Excessive Blu-ray problem
Nowadays, most white LEDs for illumination use blue light chips, which directly emit blue light. After blue light is excited by YAG yellow phosphor, part of it is converted into yellow light, and white light is synthesized together with blue light. Unlike the white light synthesized by the three primary color phosphors, the same correlated color temperature and color coordinates, the LED emits much more blue light than the three primary color fluorescent lamps. First, let's take a look at the output spectrum of the LED.
At present, the barrier layer and radiation spectral parameters of the mainstream GaN chip are: barrier potential: 2.62 ~ 2.74V, corresponding radiation photon energy: 2.62 ~ 2.74eV, radiation spectrum center wavelength: 450 ~ 470nm, the corresponding viewing function is: 0.091 ~0.038, half width of the radiation band: 30 nm.
When the radiation spectrum excites the YAG yellow phosphor to mix blue light, the emission spectrum of Figure 1 is formed. The left peak in the figure is the LED emission spectrum, and the right peak is the luminescence spectrum of a 450 nm excitation yellow phosphor. Yellow phosphors do not easily absorb blue photons. If the YAG technology is excited at 450 nm, a light efficiency of 200 lm/W is required, and the conversion efficiency needs to reach 60%. At present, the conversion efficiency of the ordinary level is only 20% to 30%. Therefore, a large amount of blue light is present in the output spectrum of the LED.
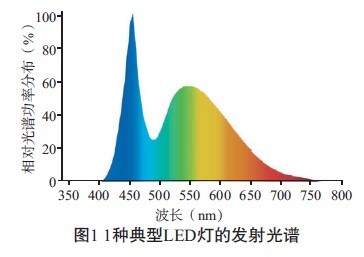
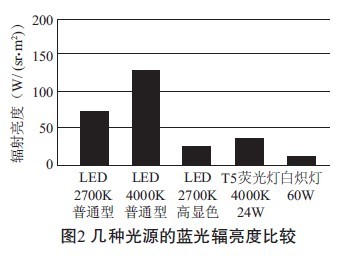
National lighting organizations agree that high color temperature white LEDs above 4 000K will cause certain harm to human biosafety and health. According to the White Paper of the GLA, the analysis of blue light components in the spectrum of LEDs, CFLs and incandescent lamps of similar color temperatures shows that the blue component of LEDs is several times that of fluorescent and incandescent lamps, and it is only 4 000K color temperature. The LED (see Figure 2), the blue light intensity of the 6 500K blue LED will be greater; and this is the data under the conditions of global integration. Since the LED is usually a narrow beam, the light in the projection area is particularly concentrated, and the local blue light intensity can reach 10 times or more of the same color temperature fluorescent lamp; at the same time, the high color rendering white LED with a color temperature of 2 700K and a color rendering index of 80 or more can be seen. The amount of blue light radiation is less than that of a fluorescent lamp that produces the same luminous flux. Therefore, a low color temperature LED with a color temperature of 2 700 to 3 000 K and a color rendering index of 80 or higher can be used indoors with confidence. But this is only the author's theoretical concept. In fact, it is unscientific to simply suppress the blue light by reducing the color temperature, which will sacrifice the light efficiency and color rendering index. Lack of red and green light, the color rendering index can only reach 62 to 63. Increasing the ratio of red light and green light will inevitably increase the cost, which will undoubtedly have a certain impact on the development of LED indoor lighting products. In order to achieve the same lighting effect as fluorescent lamps in the field of indoor lighting, the biosafety risk of LED light sources cannot be increased to reduce costs. Unfortunately, there are no LED development companies in China that have conducted risk assessments.
1.2 Generation of uneven color space
It can be seen from the spectrum of white light emitted by ordinary LEDs that the outstanding problem of white light output by this method is that LED has a halo effect and is not popular in some cases. This is due to the directional light emitted by the LED, converted by the yellow phosphor, and the Lambertian behavior, which is the spatial uniformity of the white LED space (Figure 3). The blue light emitted from the normal direction is the strongest and the least absorbed by the powder. From the current measurement method, when we measure the LED light source, the color rendering index obtained is only the average color rendering index of the color space. Similarly, the correlated color temperature value obtained is only the average color temperature of the light space. This color space distribution is bound to affect our accurate judgment of the true color consistency of the items.

2 photobiological hazards of blue light
2.1 Current general consensus
Although the development of LED is very good, it must be considered for human health, vision and biological effects. In particular, excessive blue light is used for indoor lighting, which has a series of effects on human physiology, psychology and optic nerve. This conclusion has long been accepted by lighting technology and photobiologists.
Lighting, from the current research results, can produce three kinds of effects: First, the visual effect, let us know the world with lightness and color, perceive surrounding objects to facilitate analysis and judgment; second, psychological effects, also brightness and chromaticity It can make people feel light and heavy, far and near, warm and cold, and likes and dislikes. At the same time, different shades of light also affect our mood. Third, biological effects can control our biological clock. This is why winter wakes up later and summer gets up earlier. reason. In terms of the photobiological effects of visible light, the number of blue light is the largest. The most common consensus is that when there is a strong blue light, people have no desire to sleep; on the contrary, when the blue light is weak, it is good for human sleep. The peak wavelength of blue light radiation has a large overlap with the retinal blue light damage characteristic curve and the human non-visual sensitivity curve. Therefore, when white LEDs are used indoors, some people worry that they will damage the retina and disturb the biological clock.
2.2 Blu-ray is a melatonin inhibitor
Melatonin is an amine hormone secreted by the pinealoid-sized "pineal body" deep in the human brain. It was previously called "pine pine voxel". Melatonin is the strongest endogenous free radical scavenger ever discovered. It is involved in the antioxidant system and prevents oxidative damage in cells. In this respect, it works more than all known in vivo substances. Recent research has shown that melatonin is the endocrine commander, which controls the activity of various endocrine glands in the body. The main effects of melatonin are as follows:
(1) Protect cells from disease. Because melatonin easily enters cells, it can serve as a task to protect nuclear DNA. If the DNA is damaged, it can cause cancer.
(2) The secretion of melatonin is circadian rhythm. After nightfall, the light stimulation is weakened, the enzyme activity of melatonin in the pineal gland is enhanced, and the secretion level of melatonin in the body is correspondingly increased, reaching a peak at 2 to 3 in the morning. The level of melatonin at night directly affects the quality of sleep. With age, the pineal gland shrinks until it becomes calcified, causing the rhythm of the circadian clock to weaken or disappear. Especially after the age of 35, the melatonin secreted by the body is obviously reduced, and the average is 10% to 15% every 10 years, leading to sleep. Disorders and a series of dysfunctions. Decreased melatonin levels and reduced sleep are one of the important signs of human brain aging.
Due to the inhibition of melatonin by a large amount of blue light in white LEDs, it is apparent that it will have an adverse effect on health.
