0 Preface
GPRS is used in personal business networks, mainly accessing web pages, sending and receiving e-mail, etc. There are certain protocols for various applications, but in industrial application fields such as industrial data transmission, users have no clear standards for optional UDP and TCP transmission Owners, equipment suppliers, and system integrators often have long discussions and tests on which transmission protocol to choose on the GPRS network. This article compares the two protocols, and discusses in depth the applicability of the two data transmission protocols in different application areas on the GPRS network from the aspects of reliability, applicability, and tariff.
1. GPRS industry application
GPRS is currently widely used in industries such as power, oil fields, industrial control, transportation, finance, securities, commerce, public safety, weather forecasting, and real-time traffic information release. Its application features are small data volume, large transmission interval, or irregular timing. send. Data transmission via GPRS network has the advantages of low cost, rapid and flexible networking, wide range, and professional team maintenance.
In application, users can choose UDP and TCP transmission protocols on the GPRS network. Since there is no clear standard, which protocol to choose allows owners, equipment suppliers, and system integrators to often have a long discussion about which transmission protocol to choose. And a lot of tests have been carried out. Almost every project has to carry out small-scale tests, which has affected the process of GPRS application in the industry. In addition to the influence of the protocol selection, the system operation effect is also affected by the network quality, usage mode, and peripheral equipment. The results of many experiments are inconsistent and cannot accurately reflect the effects brought by the choice of TCP / UDP protocol. Let TCP / UDP choose to fall into a new round of discussion and testing process again.
2. Comparison of the definition and main features of the two transmission protocols
For detailed explanations of UDP and TCP, please refer to the relevant materials. Here we will explain the characteristics of industry applications.
UDP is a simple datagram-oriented transport layer protocol: each output operation of the process generates exactly one UDP datagram and assembles it into an IP datagram to be sent. The format of UDP datagram encapsulated into an IP datagram is shown in the figure:
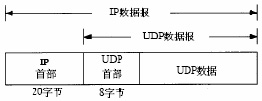
UDP does not provide reliable connections: it sends the data that applications pass to the IP layer, but there is no guarantee that they will reach their destination.
Both TCP and UDP use the same network layer (IP). TCP provides a reliable connection-oriented byte stream transport layer service. as the picture shows:
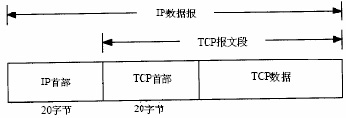
TCP provides completely different services to UDP from the application layer. TCP provides a connection-oriented, reliable byte stream service. TCP packages user data to form a message segment; it starts a timer after sending data and waits for data confirmation from the peer; the other end confirms the received data, reorders out-of-order data, and discards duplicate data; End-to-end flow control, and calculate and verify a mandatory end-to-end checksum.
Connection-oriented means that two applications that use TCP (usually a client and a server) must establish a TCP connection before exchanging data with each other. This process is very similar to making a phone call, first dialing the ring, waiting for the other party to pick up the phone and say "hello", and then explain who it is.
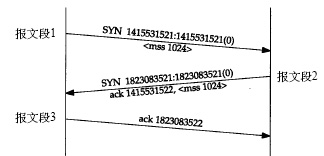
TCP transmission protocol connection process:
First establish a connection, TCP uses three segments to complete the connection. This process is also called three-way handshake. as the picture shows:
It takes 4 handshake to terminate a connection. as the picture shows:
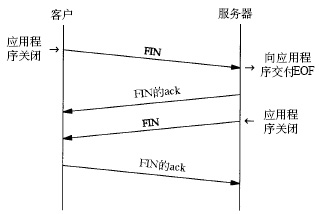
Data transmission must be confirmed by the receiver, and there are guarantee mechanisms such as timeout retransmission, which is the basic reason for TCP transmission to be guaranteed.

It can be seen that to complete a data transfer, in addition to completing the connection and terminating the connection, at least one data packet and one ACK packet are required.
UDP and TCP provide different transmission methods and different transmission qualities, and TCP provides transmission guarantee by increasing network overhead. In the actual test of GPRS network, when the network is normal, from the path of GPRS DTU-> GPRS network-> Internet-> user data center, the effectiveness of UDP transmission is> 99%, and the effectiveness of TCP transmission is ≈100%
3. Transmission efficiency
When only UDP / TCP packets are considered, application data is sent, and the data packet is an IP header + UDP / TCP header + application data. GPRS network billing is based on flow rate billing, data transmission efficiency is very important. Since the current packet data fare is calculated based on the network protocol layer 2 or higher data (ie IP packet data), the transmission efficiency calculation is calculated according to the following formula:
Packet transmission efficiency = data length / (data length + UDP / TCP header length)
Data length | UDP efficiency | TCP efficiency |
8 | 50.00% | 28.57% |
16 | 66.67% | 44.44% |
32 | 80.00% | 61.54% |
64 | 88.89% | 76.19% |
128 | 94.12% | 86.49% |
256 | 96.97% | 92.75% |
512 | 98.46% | 96.24% |
1024 | 99.22% | 98.08% |
Through the analysis of the protocol content, it can be seen that the amount of user data transmitted in a single packet is relatively small, and the transmission efficiency of the UDP protocol is significantly higher than that of the TCP protocol. The amount of application data in the industry is relatively small. When choosing protocols for different industry applications, you need to carefully analyze the number of single-frame bytes of the application layer data.
The above is just the transmission efficiency of data packets. The TCP protocol also requires additional overheads such as connection, termination, and ACK packets. The actual transmission efficiency difference between UDP and TCP will be much larger than the calculation efficiency difference in the above table.
4. Network carrying capacity
GPRS packet service channels can adopt different coding methods of CS-1 ~ CS-4 (the data rates are 9.05kbit / s, 13.4kbit / s, 15.6kbit / s, 21.4kbit / s). When the coding method is CS-4, and the wireless environment is good and the channel is sufficient, the theoretical maximum rate supported by the GPRS network can be 171.2kbps. This rate can fully support some multimedia image transmission services that require higher bandwidth. Application business. However, the actual data transmission rate is affected by factors such as the network coding method and terminal support. The receiving reference sensitivity of CS-3 and CS-4 is low. These two coding methods can only be true in areas that are close to the base station and have good signals. use.
Currently, GPRS uses the CS-2 channel coding scheme. Ensure that more than 90% of the coverage of the cell is met and meet the requirement of C / I not less than 9dB. In the cell, the uplink and downlink are provided as 1 ~ 4 GPRS channel (PDCH). At the beginning of the GPRS wireless channel allocation, at least one static packet data service channel is set, and then the PDCH allocation is adjusted according to the GPRS traffic. According to the principle of voice priority, dynamic channels will be preferentially assigned to voice channels to ensure GSM quality. So the GPRS bandwidth is 13.4Kbps ~ 54.4Kbps.
On China Mobile's GPRS network, channels are allocated asymmetrically using uplink and downlink, with small uplink and large downlink, usually 1 + 2, 1 + 3, 2 + 4, etc. This is mainly set for customers to access the Internet, and in industry applications, the situation is reversed, the uplink data is greater than the downlink data. Therefore, when considering the problem of GPRS network bandwidth, the narrower upstream bandwidth should be considered.
The characteristic of the GPRS service is the sharing of data channels, which brings the convenience of charging by traffic. However, in the community, the number of terminals is large and the amount of data is large. The terminals must compete in the limited bandwidth, resulting in a high dropout rate. Difficulties in accessing the Internet. This is also the new application feature that GPRS has shown a year after its opening: GPRS is not very competitive in the personal user market, but it has a very strong advantage in a large number of industry data transmissions.
The limited bandwidth resources impose requirements on applications: small data volume and high transmission efficiency.
5. Demand for industry applications
GPRS industry applications, whether it is power meter reading, pipe network monitoring, meteorological collection, financial services, etc., are communications between terminal equipment and data servers. Before providing GPRS transmission methods, there are radio stations, MODEM (telephone lines), and dedicated lines , Direct cable connection, etc. The communication quality provided by these methods varies greatly. Different applications have different requirements for transmission reliability, some can accept a small amount of data loss, some must ensure that no data is lost, and some do not accept time-out data. In different applications, the same feature is that it does not depend on the data protection provided by the transmission method. There is a separate communication protocol between the terminal and the data center, and the method of error / timeout retransmission ensures the safety and accuracy of the data.
The UDP protocol is used for transmission. UDP packets are equivalent to application data packets, and there is basically no additional overhead.
The TCP protocol performs multi-packet unified confirmation in accordance with the protocol window, which can reduce the number of ACK messages. However, in industry applications, the application is characterized by a small amount of data, and the transmission interval usually ranges from a few seconds to several hours. The sending interval between messages usually exceeds the maximum acknowledgment interval required by the TCP protocol, resulting in almost every data message requiring an ACK message in the TCP protocol.
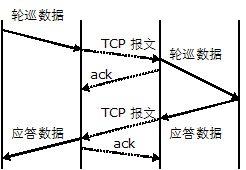
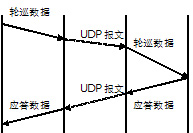
In the entire application system, the transmission guarantee is completed by the application protocol and the network protocol. It is necessary to fully use the advantages of the application protocol and the network protocol to achieve the highest overall efficiency and the best effect. Most of the application protocols have basic transmission guarantee functions. Through the application layer protocol overtime retransmission and other functions, it can fully meet the processing of small packet loss in the UDP protocol. According to the probability of UDP packet loss, the probability of retransmission is also 1 %about. If the TCP protocol is selected, the data volume will be greatly increased. The transmission process of the two protocols is shown in the figure.
6. Other issues to consider
The TCP connection guarantees the reliability of data transmission. Each specific TCP implementation must choose a MSL (Maximum Segment LifeTIme) of the message segment. It is the longest time in the network before any segment is discarded. We know that this time is limited. RFC 793 [Postel 1981c] states that the MSL is 2 minutes. However, commonly used values ​​in implementation are 30 seconds, 1 minute, or 2 minutes. For some real-time monitoring systems, the data beyond the time limit is of no use. Using a UDP connection, when the network is congested, some packets are dropped, but it can improve the situation where the received data is seriously lagging.
The application of GPRS in the power system has just started, and is in a small-scale trial stage. No matter whether UDP or TCP protocol is used, there will be no obvious pressure on the network and server system. When using the TCP protocol, reliable transmission is more convenient. But the TCP protocol is not suitable for large-scale use. For applications such as urban power distribution automation and meter reading, a system may have tens of thousands of terminals. If a TCP connection is selected, the server needs to complete the TCP connection maintenance for a large number of GPRS terminals in addition to a large number of data processing functions. This puts strict requirements on the carrying capacity of the server.
If the number of terminal connections is large, using the TCP connection protocol may bring more serious problems. After the GPRS terminal establishes a TCP connection with the server and sends data, or after the server sends a SYN + ACK response message to the terminal requesting the connection, it may not be able to receive the ACK message from the peer. In this case, the sender will generally try again. Waiting for a period of time to terminate this connection, generally speaking, this time is about 30 seconds to 2 minutes; an abnormal terminal causes one thread of the server to wait for 1 minute is not a big problem, but if the network congestion causes a lot of this situation, the server side It will consume a lot of resources in order to maintain a very large semi-connected list. Even simple saving and traversing will consume a lot of CPU time and memory, not to mention retrying the IPs in this list. If the server's TCP / IP stack is not strong enough, the end result is often a stack overflow and crash. Even if the server system is powerful enough, it is busy processing TCP connection requests and retransmitting data, which results in a serious degradation of system performance. A large amount of retransmitted data further exacerbates the congestion of the GPRS network. In severe cases, it can cause the GPRS network and server system to collapse.
7. Conclusion
In industry applications, you need to carefully analyze the characteristics of industry applications and choose UDP or TCP protocols as needed. For applications with multi-point dispersion, small data volume, high real-time requirements, and a large number of terminals, the UDP protocol can be considered. For some large amounts of data, very strict data reliability requirements, a small number of terminals, and some special applications, TCP will be better.
references:
1. "Detailed Explanation of TCP / IP, Volume 1: Protocol"
2. "H711x GPRS DTU User Manual"
Jilin Province Wanhe light Co.,Ltd , https://www.wanhelight.com
