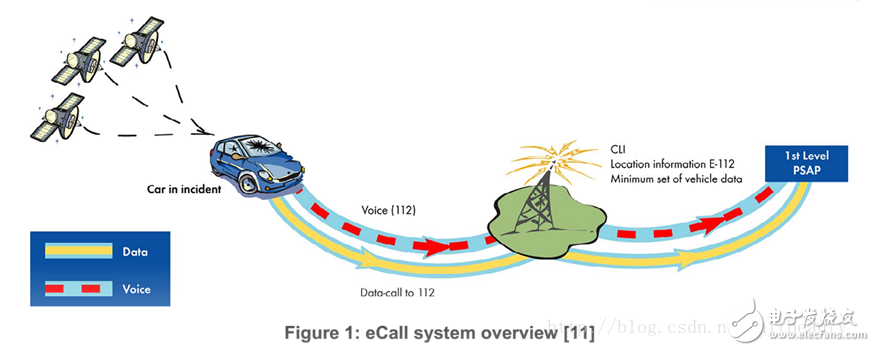
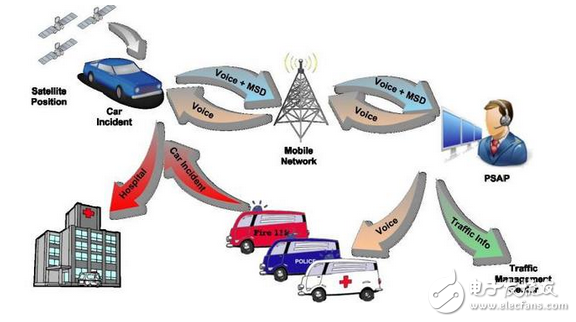
The basic principle of eCall can be described as: In the event of a car accident, the in-vehicle system automatically makes an emergency call and sends the information about the car accident to the call center through the voice channel.
There are 3 nouns in it. They are often used when reading English documents. The translation is as follows:
Car System: In-Vehicle System (IVS)
Call Center: Public Safety Answering Point (PSAP) (scientific name is Public Safety Response Center, which can be understood as 110 service desks in China)
Related information: Minimum Set of Data (MSD)
The content of the MSD message can include: location information, time, number of passengers, license plate number, and other information needed for emergency rescue.
There is one point to explain here, and it is said that information can also be sent through the data channel, but the standard has not yet been determined.
It is precisely because of the car accident that the service center can immediately receive information on the accident, so it can quickly start the rescue operation, thus reducing casualties.
The eCall system can automatically transmit the model number of the vehicle, the type of vehicle, the diagnostic information of the vehicle, and the location information of the vehicle in an emergency. PSAP (Public Safety Answering Point) or TPSP (Third Party Service Providers) can timely send relevant rescue teams to take rescue measures based on this information. In addition to the EU's mandatory support for eCall in April 2018, Russia has also begun its ERA-GLONASS requirements based on the Glonass system, which is actually the Russian version of the "eCall" system.
1. eCall standard
At present, eCall's standards mainly include three types of standards, one is the European eCall standard, and the other is the Russian ERA-Glonass standard. This standard is based on the European eCall standard, and one is Japan. standard.
2. The way eCall initiated
There are two ways to initiate eCall, one is the initiative. This method is initiated by the person on the car actively triggering the eCall button on the car. Another way is to passively initiate. For example, the sensor on the vehicle triggers the dialing of the eCall phone due to a traffic accident. When these two types of eCall are triggered, the data field sent from the car to the PSAP or TPSP will indicate whether it is a manually triggered or passively triggered eCall.
3. Data transmitted by eCall
In the European standard eCall, when the phone is triggered, the data transmitted from the car to the PSAP or TPSP is called the MSD (Minimum Set of Data). These data are the limit data required for rescue and the like. In order to ensure the timeliness and security consistency of eCall transmission data, the European eCall standard requires that the modem on the vehicle must meet the In-band modem standard defined in the eCall standard (specifically defined in one of the 3GPP standards). At the same time, the PSAP and TPSP servers also need to integrate In-band modems.
The standard MSD data has 140 bytes. After the eCall dials, the system will first transmit the MSD data before turning on the voice call.
The European standard eCall MSD includes the following data:
Message identifier
2. Reason for eCall trigger: automatic trigger or manual trigger;
3.eCall type: true eCall or test eCall;
4. Vehicle type: car, bus, etc.;
5. The unique identification number of the vehicle;
6. Fuel tank type;
7. Time stamp;
8. Car position information: that is, the latitude and longitude information of the car;
9. The accuracy of the location information;
10. The direction of travel of the car;
11. The recent historical location of the car (optional);
12. Number of passengers (optional);
13. In addition to the above optional information;
The biggest difference between eCall and regular emergency calls is:
1. Will automatically call (of course, you can also manually)
2. To achieve this, there must be a collision detection device in the vehicle system. When the device detects a traffic accident, it immediately initiates an eCall call.
3. Will send MSD data
The MSD data written in front includes location information, time, number of passengers, license plate number, and other information related to car accidents. It is essentially all the information needed for rescue. The sending of MSD data has the following characteristics:
a. The MSD starts transmitting after the eCall is connected, earlier than the voice call. That is, the call center does not talk to the owner after receiving the MSD data.
b. The call center can also request to receive MSD data again during the voice call process.
c. During the MSD transmission, the phone is muted.
d. There are two modes for sending MSD, push mode and pull mode: the MSD transmission initiated by IVS is Push Mode, and the PSAP is initiated by Pull Mode.
eCall has 2 major standards:
• PAN-EUROPEAN: EU standards
• ERA-GLONASS: Russian standard, which can be seen as one of the components of the GLONASS satellite positioning system in Russia.
among them,
EU standards are fully compliant with 3GPP standards
Russian standards are compatible with EU standards, but there are some differences, mainly:
• The Redial mechanism is different
• The MSTI's opTIonal data is different, and Glonass has more optional data.
• If the MSD fails to send, you can resend it with a short message.
3GPP standards:
• ETSI TS 126 267: ecall definition
• ETSI TS 126 267: ecall code
• ETSI TS 126 267: ecall certification
GLONASS standard:
There are many files in Russia's GLONASS satellite positioning system, and related to eCall.
• GOST 32450-2013: Global Satellite Navigation System - Automotive Transportation Navigation Equipment - Technical Requirements
• GOST R 54721-2011: Global Satellite Navigation System - Road Accident Emergency Response System - Basic Service Description
• GOST R 54618-2011: On-board emergency call system—Electrical compatibility, environmental and mechanical resistance requirements compliance test method
• GOST R 54619-2011: Data Transfer Protocol for Vehicle Emergency Call System and Emergency Response System Infrastructure
• GOST R 54620-2011: Vehicle Emergency Call System - General Technical Requirements
• GOST R 55530-2013: In-vehicle emergency call system function test method and data transfer protocol
• GOST R 55533-2013: In-vehicle emergency call system – test of wireless communication module
American Motors Replacement,Oil Filters for American Cars,Oil Filters for American Auto Motors,American Motors Replacement Oil Filters
Zhoushan Shenying Filter Manufacture Co., Ltd. , https://www.renkenfilter.com
