Due to increased demand, it is expected that the downward trend in PV module prices will weaken in the second half of 2012. This is good news for the hit solar industry.
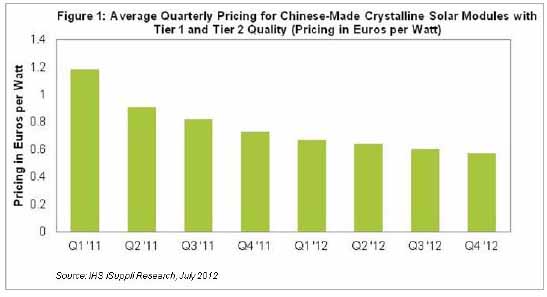
It is expected that the average market price of crystalline solar modules will still fall by 11% in the second half of the year, but the decline will be slightly less than 12% in the first half of the year and much lower than 20% in the second half of 2011. It is expected that the average market price in the fourth quarter of 2012 will fall from 0.64 euros per watt in the second quarter to 0.57 euros. Modules are usually denominated in euros, while silicon is denominated in dollars.
Figure 1 shows the average price of primary and secondary silicon solar modules produced in China.
Although the overcapacity continues to suppress the price of the entire solar energy supply chain, the photovoltaic market is finally showing signs of improvement. Not only did the global installation prospects continue to increase in 2012, but Taiwan’s battery makers also reported demand growth in June. These factors help prices stabilize and slow down.
The increase in market demand of Taiwan's battery manufacturers is one of the reasons for the steady price of photovoltaic cells. Earlier this year, the Chinese module sold in the US market was subject to a 30-250% punitive tariff, forcing Chinese companies to purchase solar cells from external sources such as Taiwan and South Korea.
However, the drop in module prices will only partially affect the solar energy supply chain. Manufacturers of vertically integrated modules will benefit from lower silicon prices, but pure module manufacturers cannot expect a significant drop in battery prices.
The module is a key component for building a complete solar system, consisting of solar cells, wires, frames and glass.
Installation plan According to IHS iSuppli's PV service, the installed capacity of global PV solar energy systems in 2012 is expected to reach 30.2 GW, which is 9% higher than the 27.8 GW in 2011. In the best case, the installed capacity may reach 36GW, which is an increase of 30% over the previous year.
The new installed capacity in Germany is expected to reach 7.3 GW this year. Although Germany's installed capacity in 2012 will be 3% lower than in 2011, the decline will be much smaller than many people worry about. Moreover, in the case of the government's downward adjustment of the subsidized electricity price (FIT), it is still expected that this relatively strong performance will be achieved. In recent years, FIT has stimulated the growth of the German photovoltaic market.
Recent developments also indicate that the German PV market has relied on government subsidies faster than many people have expected. The country’s supermarket chains have already started investing in photovoltaic systems. Their goal is clear: generating electricity for their own use. For some of these projects, the cost savings from the use of solar energy have replaced FIT and become the main reason for investing in PV installations.
Overcapacity Although the market expectation has improved, the photovoltaic industry still faces the problem of overcapacity.
The latest forecast of IHS iSuppli Company shows that in 2012, the module production capacity in overall operation will reach 49.4GW, and the battery production capacity will reach 43.5GW. Both are much higher than the expected global installation capacity of 30.2GW this year.
Considering the current integration process and the huge potential for global demand growth, IHS expects the overcapacity situation to begin to improve significantly in 2013. The second half of 2013 may mark the beginning of a new investment cycle for the photovoltaic industry.
It is expected that the average market price of crystalline solar modules will still fall by 11% in the second half of the year, but the decline will be slightly less than 12% in the first half of the year and much lower than 20% in the second half of 2011. It is expected that the average market price in the fourth quarter of 2012 will fall from 0.64 euros per watt in the second quarter to 0.57 euros. Modules are usually denominated in euros, while silicon is denominated in dollars.
Figure 1 shows the average price of primary and secondary silicon solar modules produced in China.

Although the overcapacity continues to suppress the price of the entire solar energy supply chain, the photovoltaic market is finally showing signs of improvement. Not only did the global installation prospects continue to increase in 2012, but Taiwan’s battery makers also reported demand growth in June. These factors help prices stabilize and slow down.
The increase in market demand of Taiwan's battery manufacturers is one of the reasons for the steady price of photovoltaic cells. Earlier this year, the Chinese module sold in the US market was subject to a 30-250% punitive tariff, forcing Chinese companies to purchase solar cells from external sources such as Taiwan and South Korea.
However, the drop in module prices will only partially affect the solar energy supply chain. Manufacturers of vertically integrated modules will benefit from lower silicon prices, but pure module manufacturers cannot expect a significant drop in battery prices.
The module is a key component for building a complete solar system, consisting of solar cells, wires, frames and glass.
Installation plan According to IHS iSuppli's PV service, the installed capacity of global PV solar energy systems in 2012 is expected to reach 30.2 GW, which is 9% higher than the 27.8 GW in 2011. In the best case, the installed capacity may reach 36GW, which is an increase of 30% over the previous year.
The new installed capacity in Germany is expected to reach 7.3 GW this year. Although Germany's installed capacity in 2012 will be 3% lower than in 2011, the decline will be much smaller than many people worry about. Moreover, in the case of the government's downward adjustment of the subsidized electricity price (FIT), it is still expected that this relatively strong performance will be achieved. In recent years, FIT has stimulated the growth of the German photovoltaic market.
Recent developments also indicate that the German PV market has relied on government subsidies faster than many people have expected. The country’s supermarket chains have already started investing in photovoltaic systems. Their goal is clear: generating electricity for their own use. For some of these projects, the cost savings from the use of solar energy have replaced FIT and become the main reason for investing in PV installations.
Overcapacity Although the market expectation has improved, the photovoltaic industry still faces the problem of overcapacity.
The latest forecast of IHS iSuppli Company shows that in 2012, the module production capacity in overall operation will reach 49.4GW, and the battery production capacity will reach 43.5GW. Both are much higher than the expected global installation capacity of 30.2GW this year.
Considering the current integration process and the huge potential for global demand growth, IHS expects the overcapacity situation to begin to improve significantly in 2013. The second half of 2013 may mark the beginning of a new investment cycle for the photovoltaic industry.
Solar Double-ended Brush,Solar Panel Cleaning System Tool,Solar Panel Cleaning Brush
GuangZhou HanFong New Energy Technology Co. , Ltd. , https://www.hfsolarenergy.com
