Behind any function, there must be hardware support, just like a digital camera is only enough to have a lens, it also needs the CMOS or CCD chip in the body, and, in the digital age, the level of this chip directly determines The grade of the camera. In the car, there are many more chips than the camera, which are called "electronic control units", which is the ECU (Electronic Control Unit). Many people think that ECU refers to the engine program, but in fact, the entire car's electronic system consists of a large number of ECUs, which are used to control various functions of the car, such as lights, entertainment systems, anti-theft systems and so on.
As the electronic degree of the car becomes higher and higher, especially the functions of automatic driving and active safety, the ECU of the car will increase rapidly. It is predicted that the ECU in the car will reach 50-70 on average in the next five years. Now, with some cars with complicated electronic structures, the number of ECUs has already exceeded one hundred. However, this article is not about how much ECU can be, but how to simplify the ECU.
From one to one to one to many
To discuss this topic, let's take the example of the most popular automatic driving. In an autonomous vehicle, it may include different sensors such as lidar, millimeter wave radar, medium range radar, front camera, and rear camera. The usual practice is that each sensor is responsible for processing data by one chip. The amount of data and the amount of calculations that support automatic driving are huge, and these chips must be deployed on a CAN bus network (the Ethernet used by Tesla is too advanced compared to them), its problem It is: the network itself is slow. How slow is it? You can see the picture below:
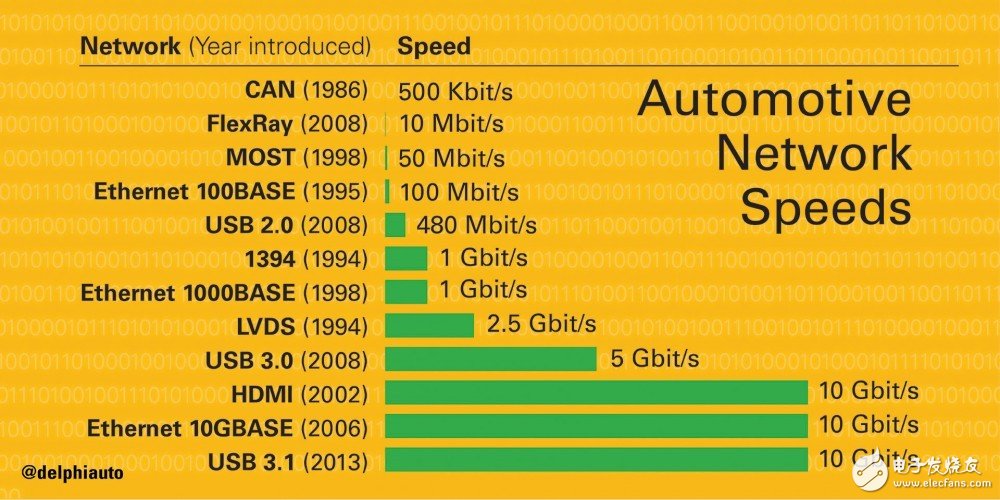
The network is slow, and the chips are distributed. The data exchange is not fast. The more chips, the lower the efficiency. How do you play autonomous driving? Turning one-to-one into one-to-one is a solution. Put these chips together and use a smaller number of chipsets or a chip with a more powerful computing power to work with those sensors. In the deployment of automotive electronic networks, this means simplification.
If you want to add more functions according to the traditional automotive electronic architecture, you need to hang more ECUs. To strengthen computing power, you have to add more ECUs. However, as the capacity of data transmission increases. Large, by increasing the number of ECUs will not work. This kind of congenital and acquired advantages and disadvantages, people who have had experience in decoration should understand, just like hydropower transformation, if the foundation is laid in the early stage, the subsequent upgrades will be much easier. This one-to-many approach can be called "MulTI-Domain Controllers" in the car, but it is not currently used in production cars. When I visited the Shanghai headquarters of the component supplier Delphi, I saw a sample of a multi-domain controller:

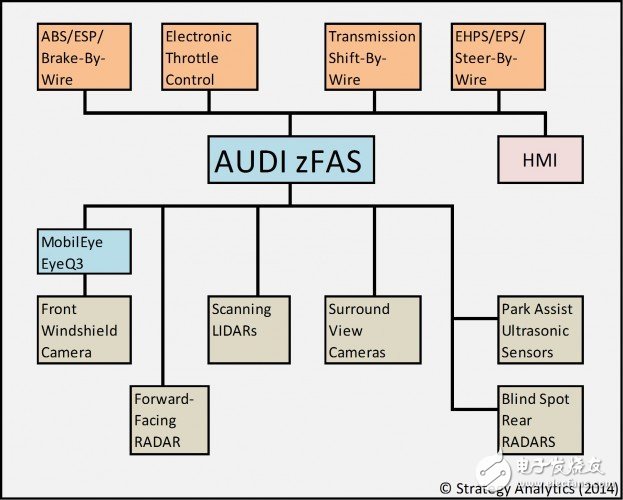
If you are concerned about automotive electronics in the past two years, you should know that Audi has exhibited an automatic driving control module called "zFAS", which can be understood as the "Audi customized version" of Delphi's multi-domain controller. Audi has shown two versions of zFAS, the second version is more streamlined and more integrated than the first version.
It looks like a motherboard. Take the second generation as an example. The integrated chips include: Altera's Cyclone V SoC FPGAs, 32-bit TriCore Tm based mulTIcore uController, Mobileye EyeQ3, NVIDIA Tegra K1 processor for complete data, planning, and decision making. Processing, and, from the sensor to this "motherboard", the data is transmitted using Ethernet. Moreover, in addition to the autopilot function, it integrates many functions related to vehicle control.
Delphi engineers also cited an example: When the LCD panel and the central control screen use the same processing chip, they will become a whole closer, and the division of labor will display different content to provide a better HMI experience.
How important is integration?
In fact, this reason is not difficult to understand. Maybe we usually buy a car and use a car to look at the appearance, power, and control. But in fact, behind these things, the car's electrical and electronic architecture is the real "skeleton." Most of the current cars still use the old bones, but the reality is that the car is becoming more intelligent, and the traditional electronic architecture is difficult to meet this demand (as already mentioned), so it needs The car uses a new architecture to deal with this intelligent trend.
Of course, stronger computing power is a must. From another point of view, it is precisely because of the increase in intelligence, the car has higher and higher requirements for electronic security, and the more integrated architecture helps to better deploy the defense mechanism. The integration of the chip means that the car really becomes a whole. If the future car is a computer + four wheels, then "a computer" means bringing together the processing chips that went for the walk (of course, not all ECUs can be integrated). They all like to say "institutions", which is actually a change in the system. After talking back to autonomous driving, as the level of automatic driving continues to increase, the trend of chip integration will become more and more obvious.
Bone Conduction Headset,Outdoor Sports Earphones,Sweat-Proof Bone Conduction Headset,Wireless Outdoor Sports Earphones
Shenzhen Lonfine Innovation Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.lonfinesmart.com
