Everything is connected. The IoT of the Internet of Things is accelerating into our daily lives and all walks of life. The connection between people and things, things and things is becoming more and more intelligent and convenient. Wireless communication becomes the Internet of Things connection. The invisible bridges, Bluetooth, WiFi, ZigBee and other mainstream communication technologies have their own advantages in the Internet of Things applications, and become a strong support for the Internet of Things.
Tektronix "Internet of Things Wireless Communication Test" will be shared by Tektronix experts in key design and test experiences such as module selection and EMI testing in Bluetooth, WiFi, ZigBee design, and help design companies and engineers to solve design problems.
Select Bluetooth module: three considerations
When choosing a Bluetooth or other RF module for an Internet of Things (IoT) device or some other project, you may find that there are many more viable options on the market than you might think. Under normal circumstances, the module manufacturer or supplier classifies thousands of modules provided based on transmission rate, transmission distance, frequency band, certification, package size, and so on.
While all-round considerations are important, some factors are even more critical. By focusing on the transfer rate, transmission distance (or coverage), and power consumption, you can effectively narrow your selection. After making a balance between these factors, choosing a module based on this can help you make decisions that directly impact the end-user experience. We will quickly examine these parameters and how they affect your device performance.
1) Transmission rate
The transfer rate or data rate is often the first thing designers and developers consider because it forces designers and developers to consider the type of information that needs to be transferred between devices. For example, the data rate required to deliver high-quality music to a headset is quite different from the data rate required for a basic heartbeat monitor.
In theory, the low-energy Bluetooth transmission rate does not support its maximum bandwidth (1 MHz) because the focus of low-energy Bluetooth is simple information transmission. If data is transmitted at a high rate, Bluetooth with low power consumption consumes more power, which is inconsistent with the original design concept. If high speed transmission is required, then consider a higher rate EDR Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Any rate increase almost inevitably consumes more power.
2) Power class and transmission distance coverage
On the manufacturer and distributor websites, the Bluetooth module is classified by category, and the category here refers to the power category. The higher the power class, the farther the transmission can reach. Like any other wireless technology, the Bluetooth network has a limited distance. The transmission distance varies with different versions.

In the same version, the supported transmission distances will still vary with different power classes. The actual signal transmission distance varies with specific environmental conditions such as transmission conditions, materials, manufacturing variations, antennas and batteries. In addition to the requirements specified in the Bluetooth standard, the equipment also needs to meet the power requirements specified by the local government spectrum regulations. For more information on these requirements, check out our previous blog post.
3) Power consumption
Power consumption is primarily related to transmission rate and distance. Since Bluetooth devices are typically battery powered, the operating current/voltage of the device is an important consideration because it directly determines the charging time and battery life.
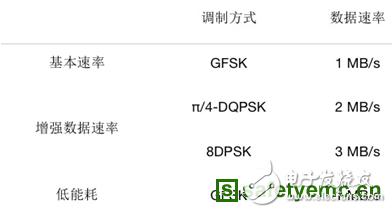
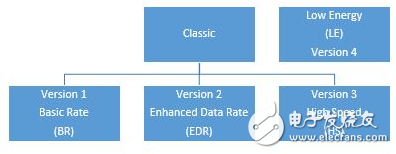
The Bluetooth SIG simplifies this early decision by further dividing the module into different versions. The Bluetooth technology version is divided into a classic version and a low power (LE) version. Economic Bluetooth versions 1, 2 and 3 are optimized for data transfer rates. In the classic version, it is divided into basic rate (BR), enhanced data rate (EDR), and high speed. Low-energy Bluetooth puts more emphasis on simple information transmission while maximizing the life of the electronics.
In addition to these classifications, the manufacturer lists the transmit and receive currents and/or power, primarily for module selection. If you can test the intended end device usage, you can more easily evaluate the module and balance the various factors in your specific application. This type of testing is further described in our power consumption blog post.
Finding the right Bluetooth module first balances the transfer rate, transmission distance, and power consumption. Once the selection is narrowed, the scope can be further narrowed down based on cost, space and compatibility. Finally, it is expected that you can use the test equipment to do some evaluation of the module. Download the Bluetooth Module Application Guide to learn more about this test.
Ensure Bluetooth design passes EMI compliance test
Before any new device supporting Bluetooth, whether it is a complete communication device or a simple USB dongle, it must meet the strict EMI radiation requirements set by the FCC.
In the past, designers typically waited until the end of the design cycle before sending the product to the test facility for formal conformance testing. Unfortunately, in many cases, many Bluetooth designs won't go through it all over again. The cost of running to the test facility several times will be very high. Depending on the root cause, it will easily lead to delays in the construction period and will not be completed on time.
A much better approach is to perform pre-consistency checks ahead of time so that any EMI issues can be identified and corrected. Intuitively, many designers believe that they do not have the equipment or expertise to complete pre-compliance testing.
Now, with modern PC-based spectrum analysis software and Tektronix's USB-based spectrum analyzers, such as the RSA306 or RSA 500/600 series, these checks are quick and easy. The video below "Basic EMI Pre-Conformance Test for Bluetooth Devices" shows how the Tektronix RSA607A Real-Time Spectrum Analyzer can be used in the lab to perform in-band and spurious signal testing.
Pre-compliance testing is important to ensure that you pass the EMI/EMC compliance test at the test facility. Bluetooth wireless testing can also be easily performed using the appropriate equipment. Watch this video to learn how to test the Bluetooth device to properly boot and transfer information. Be sure to download our RF Signal Electronic Guide to quickly identify the signal you are looking for.
This article introduces the selection of Bluetooth modules and EMI pre-compliance testing. This is a problem that engineers often face when designing Bluetooth modules, and it is often a headache. The options are much more than you might think. The focus is on the transfer rate, transmission distance (or coverage), and power consumption, which can effectively narrow the selection. EMI pre-compliance testing can effectively reduce design development time and cost.
ac dc adapter,dc adapter,ac adapter 12v,dc power adapter,ac dc adapter 24v
FOSHAN SHUNDE KELICHENG POWER SUPPLY TECHNOLGY. CO,LTD , https://www.kelicpower.com
