It just looks like a very ordinary mixer, but in reality it's as hard to control as the devil (this is the kind of devil that doesn't give money), it will make your carefully crafted tracks. All destroyed. If the gain process is set up indiscriminately, that is, the gain from the signal input to the various parts of the line at the final output of the signal, it will cause unexpected distortion, "click" sound, and many other annoying strange sounds.
However, simply reducing the signal level is not the key to solving the problem. If the gain on the signal level is too small, the inherent noise level of each device will be audible, and you will hear a lot of noise as if you had a very large gain. The trick at this point is to use enough gain to keep the sound clean and vibrant, without causing distortion or "click" sound, without damaging the sound quality and clarity of the sound.
Treating a typical sound signal, if you use the following method, it will be difficult to operate, that is, use a microphone to pick up the signal, then pass the microphone preamp, some channel faders, an auxiliary send, an effect processor, the main fader, Finally, it is input to the input of the recorder.
If you want to make the recording work more concise and more effective, you should pick up the sound signal from the microphone (or the sound level of the electronic instrument output line) and input it directly into the recorder. Then gradually adjust the equipment in the next steps. Gain process.
- Microphone. The signal line starts at the source of the sound, so if your microphone doesn't work, then nothing is going on.
Dynamic microphones can withstand large input levels without distortion, but if you are using a sensitive condenser microphone, be sure to keep the signal clean and clear. The impact of loud sounds from snare drums, guitar amps, singers, and other more dynamic sound sources can cause distortion in the microphone, which can be heard.
Many condenser microphones have an attenuation switch of at least 10dB, so when you hear a "beep" in the midrange range or a noise in the high frequency range, turn this switch on (the low frequency range of the microphone is usually the case) It’s all due to the singer’s “blowing†of the microphone).
How to set the correct gain process
If the distortion persists, move the microphone a little further away from the high sound source. If the microphone can't pick up the sound at this time, it may be that you have chosen the wrong type of microphone - this microphone is not suitable for your current work.
- An instrument with line output. What are the problems with simply adding the sound of a bass, guitar, keyboard, or other sound source module to the mix?
The problem is a lot. Since the electronic instrument has a built-in preamplifier, if you suddenly turn the volume too loudly, you will hear a slight scream. When this happens, you should adjust the line output level of the electronic instrument to 75% of the maximum volume level.
- Microphone/line preamplifier. What we are going to talk about is really the kind of thing that will get you into trouble. How to set up the microphone/line preamp on your mixer.
If you screw all of these gain knobs to their maximum values, you will definitely hear very severe distortions and “clicksâ€, especially if the rear-stage amplifier you choose is a cheaper product. . When the mixer's fader is raised to a higher position or the volume of the amplifier is louder, all the annoying sounds will jump out.
To avoid this, the most effective solution is to set the magnitude of each gain to 75% of the maximum gain value. If the situation still does not improve after you do this, turn on the channel attenuation switch on the mixer (assuming this feature is available on your mixer). If there is no such button on your mixer, reduce the power of the previous stage until the distortion disappears.
How to set the correct gain process
- Channel faders. The next step in the gain adjustment is the fader of the mixer. Obviously, it is very important to use a fader to balance the preamplifier of the microphone/line. Here, I can recommend a better adjustment scheme for you:
Place the fader at 75% of the maximum level. Then, slowly raise the amp/line preamplifier until the signal level is appropriate (we will discuss the recording level later).
Listen carefully to see if there is a "beep" or distortion. In the most ideal case, the sound is very powerful and energetic when you adjust the position of the fader and the preamplifier of the mic/line to 75% of the maximum volume.
If you have to adjust the fader or the amp/line preamp to almost the maximum volume during operation (you may be recording a whisper or other extremely faint sound), then You must listen very carefully to confirm that the sound is satisfactory. Who should you upgrade to this situation, preamplifier or fader? The final answer depends on the degree of distortion in your device and the judgment of your ears as you continue to experiment.
- Group faders. You can group several signals for an auxiliary mix, such as combining the background vocals of several tracks into a single stereo track, or sending a single track to a stereo input. End - add other signals.
Still, we have to abide by the "75%" rule mentioned above. If you are experiencing sound distortion, you can reduce the faders, group faders, and mic/line preamps for each channel separately until the sound distortion problem is resolved.
There are 3 gains to adjust here, you have to constantly adjust and listen carefully.
- Effects processor. When you connect the effects processor to the line through the secondary sender, the situation becomes more complicated.
First, use the "75%" rule to adjust the auxiliary send level knob to 75% of the maximum level. Then check if the input level of the effect is broken. This is not a simple matter, at least more complicated than letting the effect sound. Because all effects will have different reactions to the input signal.
For some devices, you will find that the level indicator has hit the red overload zone and the sound is still very clean. For other devices, the level indicator just touched the red area, the sound is no longer necessary (speaking too much, but at least the sound is distorted). Until you fully master the characteristics of an effect, you can properly adjust the input level and use it safely.
If you find that the input level is too low, that is, the "click" and "digital" sounds are already audible, adjust the input level to approximately 75%. At this time, you should be careful not to let the red overload indicator light up too much. When you set the appropriate level, don't think about the lights anymore. Just listen with your ears.
Home studio recording expert Joe Meek’s point of view on this issue is: “If the sound sounds good, then it’s good!â€
- Analog recorder. Mixing work on an analog recorder is a more tolerant job. In most cases, you can allow the pointer to hit the red overload zone, and the sound is the best. This seems to be a bit contrary to the famous sayings we have heard on weekdays, but as long as you try it yourself, you will understand.
However, depending on the characteristics of your recorder and the characteristics of the tape used, the above-mentioned "Red Overload Zone" rule may also bring you terrible sound distortion. But then again, following this rule usually gives you a very powerful and energetic voice. How to use it, let your ears make a ruling.
- Digital recorder. Compared to analog recorders, digital recorders do not have the slightest tolerance. If you are using a digital multitrack or DAT to record, the level pointer hits the red area, or if you exceed a certain point, then your recording will fail.
There is a rule that always applies, a very simple rule: be sure to keep the level below the red overload line!
There are two basic ways to keep your voice from being distorted. The first method is to limit the level of the track, or to thoroughly grasp the volume range of the sound source, and then set the maximum level of the track. The second method requires you to have plenty of time and great patience to play back and forth over and over again until all the volume has reached the required level.
There is a more courageous way to set the input level just below the overload point and then start praying. Obviously, the more familiar you are with the dynamic range of the instrument, the more effective the means you can use.
- The last tip. You have to learn to believe your ears, not to trust the meter. In fact, you can't guarantee that the volume indicator or the LED indicator on the music device is completely correct, but you must be able to hear the flaws in the sound. Those who die and hold the indicator can't record a good voice (think about it).
Also note that using the equalizer on the preamp or mixer will affect the gain of the device, so in practice, you must perform one step (such as boosting certain bands), verify it. What happened to the sound.
Finally, remember that when the recording indicator lights up, the musician's performance will become more powerful and powerful. So when you check the volume and set the basic level, don't fully believe the sound size of the player at this time. When the recording is official, the volume is likely to be 2 dB to 5 dB larger than this. The simple solution is to leave a certain amount of margin in advance, and you will benefit from it.
- Glossary:
Clipping: Overloaded. That is, we heard the sound of "å™—å™—". This distortion occurs when the audio signal passes through the device if the signal level exceeds the maximum level that the device can withstand.
Gain Stage: Gain progression. Set an acceptable maximum level of distortion without distortion in various parts of the signal line.
Headroom: We call it the headroom. The dynamic space between a device's usual level and the maximum signal level it can withstand without distortion.
Noise Floor: The inherent noise level (also known as the noise floor). The noise floor generated by the various components on the line without any signal input.
High Frequency PCB - Definition, Characteristics, Manufacturing, Materials and Application Scenarios
With the development of science and economy, the electronic industry has become an important driving force for economic development. Electronic products have become a part of life, affecting people's way of life. High-frequency circuit boards are widely used in many electronic industries and some instruments and equipment, and high-frequency PCB applications are also increasing. Choose high-frequency circuit board manufacturers in good service to buy high-quality products for use, we have to understand the relevant knowledge of high-frequency board.

What Is A High Frequency Circuit Board?
High frequency circuit board (HF PCB) is a special circuit board with high electromagnetic frequency. Generally speaking, high frequencies can be defined as frequencies above 1GHz. Its physical performance, accuracy and technical parameters are very demanding. It is often used in automobile anti-collision system, satellite system, radio system and other fields.
High Frequency PCB include:
- Rogers high frequency PCB
- Power amplifier high frequency PCB
- Buried blind hole mixed high frequency PCB
- Ceramic high frequency PCB
- Ceramic mixed high frequency PCB
- Communication antenna high frequency PCB
- GPS antenna high frequency PCB
- FR-4 high frequency PCB
- Double sided high frequency PCB
- Microwave High Frequency PCB
- Induction High Frequency PCB
- 2.4G Radar Induction PCB
- 5.8G Microwave Induction PCB
The utility model patented high frequency circuit board includes a core board with a hollow groove and a copper clad plate adhering to the surface and the lower surface of the core board by flow glue. The upper opening and the lower opening edges of the hollow groove are provided with a baffle.
The high frequency circuit board provided by the utility model is provided with a barrier which can block the flow glue at the upper and lower edges of the hollow groove of the core board.
In this way, the flow glue will not enter the hollow slot when the core plate is bonded with the copper clad laminate placed on the upper and lower surfaces, that is, the bonding operation can be completed by one press.
Compared with the existing technology, the high frequency circuit board can only be completed by secondary pressing. The high frequency circuit board in the utility model has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and easy manufacture.
Characteristics of High Frequency Circuit Board
Generally speaking, high frequency circuit boards have their own characteristics: low dielectric constant, relatively stable. In theory, the smaller the dielectric constant, the more stable the signal, and the higher the frequency circuit board can play a better role in signal transmission. Medium loss is very small, it is not easy to absorb water and moisture, heat resistance, corrosion resistance and other excellent performance. Conversely, if the dielectric constant is high, the signal transmission process is slow.
The thermal expansion coefficients of high frequency circuit boards and copper foil are also correlated to a certain extent. They are consistent as far as possible. The inconsistency can easily lead to the separation of copper foil in the alternate change of heat and cold. The later use will affect the signal transmission of PCB. The absorbency of high frequency circuit board is lower than that of other multi-layer circuit boards, because humidity will affect the dielectric constant and dielectric loss of high frequency circuit board. In addition, the heat resistance, chemical resistance, impact strength, peeling strength and other requirements are also good.
High frequency signals are vulnerable to noise and come with much tighter impedance tolerance as compared to conventional circuit boards.

High Frequency Circuit Board Materials
High frequency PCB have their own unique plates. Special materials are used to attain the high frequency given by the High Frequency PCB. PCB manufacturer commonly used Materials are: rogers(Rogers 4350B HF.Rogers RO3001.Rogers RO3003).Taconic(RF-35 Ceramic.TLX). Arlon(85N).Isola(IS620 E-fibre glass).F4B.TP-2.FR-4,Dielectric constant 2.2-10.6 and so on. FR4 is the cheapest one, while Teflon is the most expensive one. But they all have a common characteristic, which is the resin used in the material. The wiring of high frequency circuit board is exquisite and has great influence on components. High-frequency signals have the strongest impact on analog devices, so we should deal with the relationship between them to achieve the best performance. Therefore, high frequency is not easy to pass through high capacity electrolytic capacitors with poor high frequency performance.
The substrate material used in the high-frequency circuit board needs to have excellent electrical properties, good chemical stability, and the loss on the substrate is very small as the frequency of the power signal increases, so the importance of the high-frequency board is highlighted.
Therefore, when selecting a substrate for a PCB for a high-frequency circuit, it is particularly necessary to examine the various characteristics of the material DK at different frequencies. For the requirements of high-speed transmission of signal emphasis, or characteristic impedance control requirements, focus on DF and its performance under conditions of frequency, temperature and humidity.
Under the condition of frequency change, the general type of substrate material shows a large change of DK and DF values. Especially in the frequency range of l MHz to l GHz, their DK and DF values change more significantly. For example, a general-type epoxy resin-glass fiber-based substrate material (general type FR-4) has a DK value of 4.7 at a frequency of 1 MHz, and a DK value of 4.19 at a frequency of 1 GHz. Above lGHz, its DK value tends to be flat. The changing trend is smaller as the frequency increases (but the change is not large). For example, at 10 GHz, the DK value of FR-4 is generally 4.15, and the substrate material having high-speed and high-frequency characteristics changes in frequency. In the case of DK, the DK value changes little, and the DK keeps changing in the range of 0.02 from the frequency of change from 1 MHz to 1 GHz. Its DK value tends to decrease slightly from low to high frequency.
The dielectric loss factor (DF) of a general type of substrate material is affected by a change in frequency (especially in a high-frequency range), and the change in DF value is larger than that of DK. The law of change tends to increase. Therefore, when evaluating the high-frequency characteristics of substrate material, the focus of its investigation is on the change of its DF value. There are two distinct types of two types of substrate materials with high-speed and high-frequency characteristics. In general, there are two different types of substrate materials: one is that the (DF) value changes little with frequency. There is also a class that, although similar in magnitude to the general substrate material, has a lower (DF) value.
High-frequency circuit boards with induction heating technology have been widely used in the communication industry, network technology field promotion and high-speed information processing systems to meet the requirements of many high-precision parameter instruments. A reliable high-frequency circuit board provides great help in actual production.
From material DF:
The circuit board material with DF between 0.01 and 0.005 is suitable for the digital circuit with the upper limit of 10Gb / S;
DF between 0.005-0.003 is suitable for digital circuits with an upper limit of 25gb / s;
Circuit board materials with DF no more than 0.0015 are suitable for 50GB / s or even higher speed digital circuits.
Common high-speed PCB materials are:
1) Rogers: ro4003, ro3003, ro4350, ro5880, etc
2) TUC: tuc862, 872slk, 883, 933, etc
3) Panasonic:Megtron4.Megtron6, etc
4) Isola: fr408hr, is620, is680, etc
5) Nelco:N4000-13.N4000-13EPSI, etc
6) ShengYi
Of course, there are many other high-frequency board materials, such as Arlon (acquired by Rogers) and Taconic, which are all old brand RF microwave material factories with guaranteed performance.
Our most common request is for FR-4 material, which is composed of woven fiberglass bound by an epoxy resin, and which we always keep stocked as one of our PCB Options at a Standard Price. FR-4 is a robust material with excellent thermal characteristics, and electrically it is known to perform quite reasonably at RF or Microwave frequency levels.
Some clients whose designs are intended for particularly demanding applications-such as high-power or broadband circuits-find that FR-4 sometimes just does not do the job at those higher frequencies. In these cases, we are always happy to help you find a laminate material to suit your specific needs, and our highly customizable PCB Assembly Process can be easily adjusted to make sure your project lead time is not impacted.
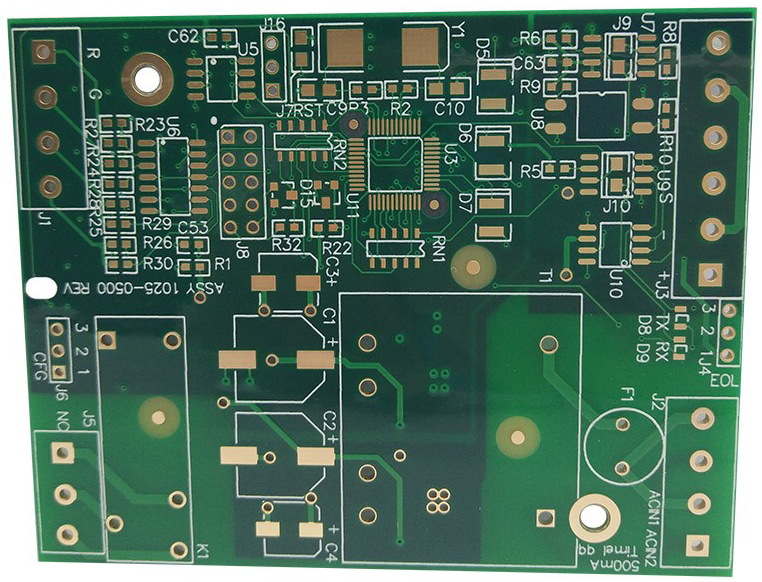
A snapshot of the datasheet for FR-4 material is shown below for reference.
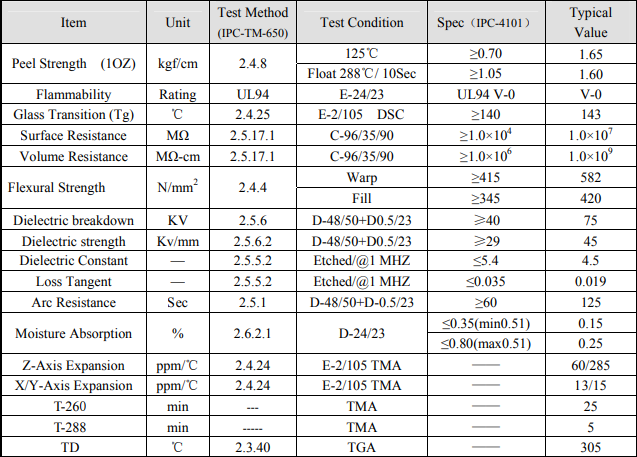
The most popular high-frequency-specific laminate materials were developed by Rogers, and referred to with an [RO-[ prefix. These high-quality materials exhibit approximately a 20% reduction in dielectric constant, compared to standard FR-4; they also boast rather impressive thermal characteristics, with Tg values above 280°C . A snapshot of the datasheet for RO4350B and RO4003C is included below for your convenience.
Requirements for Manufacturing Materials of High Frequency PCB
1. Dielectric loss (Df) must be small, which mainly affects the quality of signal transmission. The smaller the dielectric loss, the smaller the signal loss.
2. Low water absorption. High water absorption will affect dielectric constant and dielectric loss when damped.
3. The dielectric constant (DK) must be small and stable. Usually the smaller the better. The transmission rate of the signal is inversely proportional to the square root of the dielectric constant of the material. High dielectric constant easily causes signal transmission delay.
4. The coefficient of thermal expansion of copper foil is the same as that of copper foil, because the inconsistency will cause the separation of copper foil in the change of cold and heat.
5. Other heat resistance, chemical resistance, impact strength and peeling strength must also be good.
Generally speaking, high frequency can be defined as frequency above 1 GHz. At present, most of the high frequencies used are fluorine dielectric substrates. Teflon is much better than other substrates, such as PTFE, which is usually called Teflon. However, Teflon substrate has the disadvantage of high cost and large heat resisting property.
How to choose high frequency high speed PCB material
To select the PCB substrate, a balance must be made among meeting the design requirements, mass production and cost. In short, the design requirements include electrical and structural reliability. Generally, when designing a very high-speed PCB board (frequency greater than GHz), PCB material problem will be more important. For example, the FR-4 material, which is commonly used now, has a large dielectric loss DF (dielectric loss) at several GHz, which may not be applicable.
For example, 10Gb / s high-speed digital signal is a square wave, which can be regarded as the superposition of sine wave signals of different frequencies. Therefore, 10Gb / s contains many different frequency signals: 5GHz fundamental signal, 3-order 15GHz, 5-order 25ghz, 7-order 35GHz signal, etc. The integrity of the digital signal and the steepness of the upper and lower edge are the same as the low loss and low distortion transmission of the RF microwave (the high-frequency harmonic part of the digital signal reaches the microwave frequency band). Therefore, in many aspects, the selection of high-speed digital circuit materials is similar to the requirements of RF microwave circuits.
The main factors to be considered in the selection of suitable base materials are as follows:
1. Manufacturability:
2. Various performances (electrical, performance stability, etc.) matching with products:
Low loss, stable Dk/Df parameters, low dispersion, small variation coefficient with frequency and environment, small tolerance of material thickness and glue content (good impedance control), if the trace is long, consider low roughness copper foil. In addition, the high-speed circuit needs to be simulated in the early stage of design, and the simulation result is the reference standard of the design. "Xingsen Technology-Agilent (High Speed/RF) Joint Lab" solves the performance problems of inconsistent simulation results and tests. It has done a lot of simulation and actual test closed-loop verification, and the simulation can be consistent with the actual measurement through unique methods.
3. The availability of materials in a timely manner:
Many high-frequency board material procurement cycles are very long, even 2-3 months; in addition to the conventional high-frequency board material RO4350 in stock, many high-frequency boards material need to be provided by customers. Therefore, high-frequency plates need to communicate with manufacturers in advance, and prepare materials as soon as possible;
4. Cost:
5. Applicability of laws and regulations:
It should be integrated with environmental protection regulations of different countries to meet the requirements of RoHS and halogen-free.
Among the above factors, the high-speed digital circuit operation speed is the main factor to be considered in PCB material selection. The higher the speed of the circuit, the smaller the DF value of the selected PCB material. The low loss circuit board will be suitable for 10Gb / s digital circuit; 25gb / s digital circuit needs to select the board with lower loss; ultra-low loss board will be suitable for the faster high-speed digital circuits, and its speed can be 50GB / s or higher.
How to Make High Frequency Circuit Board?

Fabrication Principle of High Frequency Circuit Board
In the design of high frequency circuit, the power supply is designed in the form of layers, which is much better than that in the form of buses in most cases, so that the circuit can always follow the path with the smallest impedance. In addition, the power board has to provide a signal loop for all generated and received signals on PCB, which can minimize the signal loop and reduce noise, which is often ignored by low frequency circuit designers.
In the design of high frequency PCB, we should follow the following principles:
- Unity of power supply and ground, stability.
- Careful wiring and proper termination can eliminate reflection.
- Careful consideration of wiring and proper termination can reduce capacitive and inductive crosstalk.
- Noise suppression is needed to meet EMC requirements.
Points for Attention in Manufacturing High Frequency Circuit Board
1. Impedance control is strict, relative line width control is very strict, general tolerance is about 2%.
2. Because of the special plate, the adhesion of PTH copper deposit is not high. Usually, plasma treatment equipment is needed to roughen the through-hole and surface to increase the adhesion of PTH copper and solder resist ink.
3. Do not grind the plate before welding resistance, otherwise the adhesion will be very poor, and can only be coarsened with micro-corrosive powder.
4. Most of the sheets are PTFE materials. There will be many rough edges when they are formed by ordinary milling cutters, which need special milling cutters.
5. High frequency circuit board is a special circuit board with high electromagnetic frequency. Generally speaking, high frequency can be defined as frequency above 1 GHz.
Its physical performance, accuracy and technical parameters are very demanding. It is often used in automobile anti-collision system, satellite system, radio system and other fields.
Scenario and Field of High Frequency Circuit Board Application:
- Communication Base Station
- Repeater
- GPS antenna
- Radio Frequency Antenna
- power amplifier
- Signal amplifier
- Wave filter
- coupler
- attenuator
- Power divider
- 3DB Bridge, etc.
Nowadays, the high frequency of electronic equipment has become a trend of development, especially in the growing development of communication networks, aerospace, military equipment, intelligent transportation, information products are also increasingly high-speed and high-frequency. Nowadays, with the development of science and economy, many new products need high frequency circuit boards. High frequency circuit boards play an increasingly important role in people's daily life.
It is not easy to find a fast and good manufacturer of high frequency circuit boards. Jinghongyi PCB has its own unique board advantages in making high frequency circuit boards. It has reliable automatic production equipment and testing equipment.
Reasons for Choosing Jinghongyi PCB
1. Top imported raw materials for high frequency circuit boards to ensure product quality from the source
- Plate: Shengyi, South Asia, KB.Rogers.Taconic. Isola. Arlon.F4BM.Nelco.Hitachi.
- Potions: Rohm&Haas (US) Atotech (Germany) Umicore (Germany)
- Ink: Taiyo (Japan)
- Dry membrane: Asahi (Japan), Dupont (US)
2. Full set of surface treatment equipment to meet the needs of various industries
We are one of the few companies in PCB industry equipped with complete surface treatment equipment.We can deal with the Immersion Gold completely.
Immersion Silver, Immersion tin, OSP, tin spraying, gold plating, thick gold plating, tin plating, silver plating and other related requirements.
3. Leading PCB Multilayer Circuit Board Technology Capability
- Maximum Layer: 28 layer
- Maximum Plate Thickness: 6.0mm
- Maximum Thickness to Diameter Ratio 10:1
- Maximum Copper Thickness: 6OZ
- Maximum working plate size: 1000x610mm
- Thinnest 4 Layer PCB: 0.33mm
- Minimum mechanical hole/pad: 0.2/0.40mm
- Drilling accuracy: +/-0.05mm
- PTH Aperture Tolerance: +/-0.05mm
- Minimum Linewidth/Line Spacing: 3mil/0.075mm
4. Strict PCB quality control system to effectively guarantee product performance
- Strictly control according to IPC standard to ensure 100% qualified rate of shipment quality.
- Implement quality PDCA cycle process to continuously improve product performance
- Imported DIONEXICS-900 and Temperature Cycle Inspection Equipment from USA to ensure high reliability and stability of products
5. Top Technical Team
Eight years of focus on R&D and manufacture of high-frequency board and microwave radar RF circuit board, with a dedicated, united and tenacious R&D team, customers NPI stage products, all into the process evaluation system, meet the evaluation criteria of the project, further review by the R&D team and file a case tracking the whole process.
The staff has 3-12 years of professional and technical personnel with multi-layer circuit board experience. They have rich experience in various industry standards and process quality requirements.
6. Intimate service
Service concept: regard customers as eternal partners, develop together, only choose reputation, not customers, regardless of the size of customers, in the case of customer needs, to provide the best service.
Flexible service: We will be eager to meet the customers'needs, think what they want, and do our best to help customers solve problems, reduce losses or promote project development.
Useful Resources
- Ten PCB Routing Rules for High Frequency Circuits
- Difference between High Frequency Circuit and High Speed Circuit
- Interference Analysis and Countermeasure in High-Frequency PCB Design
High Frequency PCB, High Frequency Circuit Board, High Frequency PCB Design, High Frequency PCB Materials
JingHongYi PCB (HK) Co., Limited , https://www.pcbjhy.com
