Every day we talk about distributed photovoltaics, but can you tell us exactly what the definition of distributed photovoltaics is? Don't laugh. Actually, many people are not sure.
First, the definition of distributed photovoltaic
Initial definition
The photovoltaic power generation facilities featured by the construction and operation of the user's site or nearby are characterized by user-side self-use, excess power grid access, and balanced adjustment of the distribution network system.
——Notice on the Interim Measures for Printing and Distributing Distributed Photovoltaic Generation Projects (Guang Neng Xinneng [2013] No. 433)
On this basis, State Grid Corporation supplemented two conditions:
1) Access below 10kV
2) The single-point scale is less than 6MW
——Notice on Printing and Distributing Distributed Power Supply Grid Service Management Rules of the State Grid
Extended definition
The distributed photovoltaic power generation project that utilizes the construction of the roof of a building and ancillary venues can be selected as a model of “spontaneous self-use, excess power access to the Internet†or “full-scale Internet access†when the project is filed.
The construction of non-power consumption facilities such as agricultural greenhouses on the ground, access to the power grid at a voltage level of 35 kV and below (66 kV in the northeast region), a single project capacity of not more than 20,000 kilowatts, and power generation mainly at the grid point The photovoltaic power station projects that were changed in the radio zone were included in the management of the scale of distributed photovoltaic power generation.
——Notice on Further Implementing the Policy Concerning Distributed Photovoltaic Generation (Guoeng Synergy Energy [2014] No. 406)
For projects below 10kV and single-point access below 6MW, both the State Grid Corporation and the National Energy Administration consider it a distributed project;
For projects with single-point access exceeding 6MW or voltage levels exceeding 10kV, the definitions of the State Grid Corporation of China and the National Energy Administration are different.
State Grid Corporation of China
Distributed power supplies include two types:
The first type is a distributed power supply with a total installed capacity of no more than 6 MW connected to a single grid point with a voltage rating of 10 kV or less.
Second type: 35kV voltage level access, annual self-use of distributed power supply greater than 50%, or 10kV voltage level access and a single grid point with a total installed capacity of more than 6 megawatts, the annual spontaneous power consumption of more than 50% of distributed power .
—— Notice of the State Grid Corporation of China on Printing and Distributing Distributed Power Grid Service Management Rules (National Grid Marketing [2014] No. 174)
In the actual project work,
On the one hand, contact with the State Grid Corporation of China and the National Energy Administration respectively;
On the other hand, due to changes in policy, the National Energy Administration currently has the same management methods for "agricultural and fishery-light complementary projects with a voltage rating of 10kV or more and a single point of access to 20MW." Preferential policies.
Therefore, it is recommended to consider "10kV or less, single-point access to 6MW."
Second, the characteristics of distributed photovoltaic
Feature 1: Located near the user
Feature two: 10kV and below access
Feature 3: Access to the distribution network and local consumption
Feature 4: The single-point capacity does not exceed 6MW (multi-point access is the maximum)
Third, the classification of distributed photovoltaic systems
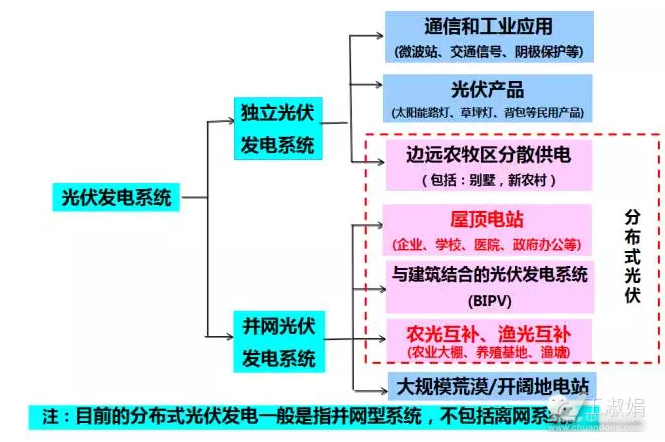
First look at the classification of photovoltaic power generation systems.
Therefore, grid-connected distributed photovoltaic systems can be roughly divided into three categories.

What needs to be emphasized is:
Although the above three types are all distributed photovoltaic projects, only BAPV and BIPV enjoy the benefits of being “not subject to scale targetsâ€; agricultural light/fish-ray complementary projects need to compete with common ground power stations. Get "scale index"!
1 rooftop power station
1. Roof of industrial plant
advantage
1) Large area, large-scale construction
2) The electricity load is large and stable, and the electricity load curve matches the characteristics of photovoltaic output, and self-use can be realized.
3) High price of electricity and high expected project income
Shortcomings
1) Business owners have different enthusiasm and rents are too high;
2) The company's 25-year payment ability and reputation;
3) Corporate holidays and maintenance will cause a certain percentage of Internet access
2, commercial building roof
advantage
1) The price of electricity is the highest and the expected return of the project is high;
2) The electricity load is stable, and the electricity load curve matches the characteristics of PV output, and self-use can be achieved. Shortcomings
1) The monomer area is small, and the large-scale development and coordination cost is high;
2) There are many roof structures, and there are many tall buildings around, and the shadow affects power generation.
3. Government office buildings and schools
advantage
1) The owners of government and school office buildings are relatively easy to coordinate;
2) The electricity load is stable, and the electricity load curve matches the PV output characteristics. Shortcomings
1) The monomer area is small and the installed capacity is limited;
2) The load on the internet is low due to low load and holidays;
3) Low self-use electricity prices are suitable for full Internet access.
4, transportation hub
advantage
1) The load is stable.
2) The price of electricity is high. Shortcomings
Need to meet the special requirements of the building;
5, residents roof
advantage
1) It is easier to coordinate.
2) There will be additional subsidies such as “Beautiful Countryside†and “PV for Poverty Alleviationâ€. Shortcomings
1) The property rights of urban rooftops are not clear, and there are many special-shaped roofs; the available area of ​​rural rooftops is small, and the bearing capacity is not clear.
2) The price of electricity is low;
3) The power load curve does not agree with the PV project output curve.
2 Agricultural light complementary project
1. Multi-story greenhouse
Features
1) High degree of integration of photovoltaics and agriculture;
2) Relatively poor insulation performance, suitable for the southern region in the middle and low latitudes. At present, it is mainly used for flowers and nursery.
2, stand-alone greenhouse
Features
1) Guaranteed the maximum use of the greenhouse area and large installation capacity;
2) Poor lighting, suitable for planting seedlings such as mushrooms.
3, additional greenhouse
Features
1) The degree of integration of photovoltaic and agriculture is not high;
2) Agricultural light does not affect each other and can fully ensure the best performance of the respective functions of greenhouse agriculture and photovoltaic power generation.
4, open greenhouse
Features
It is a favorable combination of agriculture and photovoltaics. It is suitable for cultivation of traditional Chinese medicine in North China, East China, and South China, as well as animal husbandry in natural forage farms.
Is a multi-question photovoltaic agriculture combination type, to solve the problem of power plant project land, there are suspected violations on the ground, the project is legitimate late, normal operation risk.
5, combined with the breeding industry
Features
When the insulation performance requirements are not high, PV modules can also be directly used as roofing enclosure materials. Seals and structural adhesives are used for waterproofing the gaps between components, and lighting strips are added as needed.
6, fisheries light complementary
Features
1) It can solve the problem of lack of land in the southeastern region;
2) Relatively high cost;
3) Inexperience in construction, operation and maintenance. 3BIPV Project
Shandong Weihai Blue Star Office Building 161kWp Optoelectronic Engineering
Time of completion: December 22, 2011
Application Type: Photovoltaic curtain wall
Baoding Diangu International Hotel 300kWp PV Project
Completed: October 2008
Photovoltaic Applications: Curtain Walls, Roofs
High cost and low power generation affect the development of BIPV
BIOTEPT Single Phase Resilient Base Motors, resilient (cradle) mounted, capacitor start-type, ball bearing motors for fan and blower service. Moderate starting torque electrical design to reduce stress on fan blades during start-up. Capacitor-type design has higher energy efficiency rating than split phase, single phase fan and blower motors. Suitable for belt-driven fans or fan-on-shaft applications. Self-ventilated design, may be mounted outside of the fan`s airflow.
Single Phase Resilient Base Motors for use where water and dust exposure is minimal. Ideally suited for use on pumps, compressors, blowers, fans, and belted applications.
Include:
DRIP-PROOF ODP • SINGLE PHASE RESILIENT BASE
TEFC • SINGLE PHASE RESILIENT BASE
PREMIUM EFFICIENCY FAN MOTORS
DRIP-PROOF • SINGLE PHASE
RESILIENT BASE



Resilient Base Motor,Single Phase Resilient Base Motors,Plit Phase Resilient Base Motor,Odp Resilient Base Motor
Ningbo Biote Mechanical Electrical Co.,Ltd , https://www.biotept.com
